Have you heard of probiotics? Those live bacteria that keep your gut healthy? Well, there’s a new player in town: postbiotics. These aren’t living bacteria themselves, but rather beneficial substances produced by our gut bacteria.
Think of probiotics as the chefs, prebiotics as their ingredients, and postbiotics as the delicious, health-promoting meals they create!
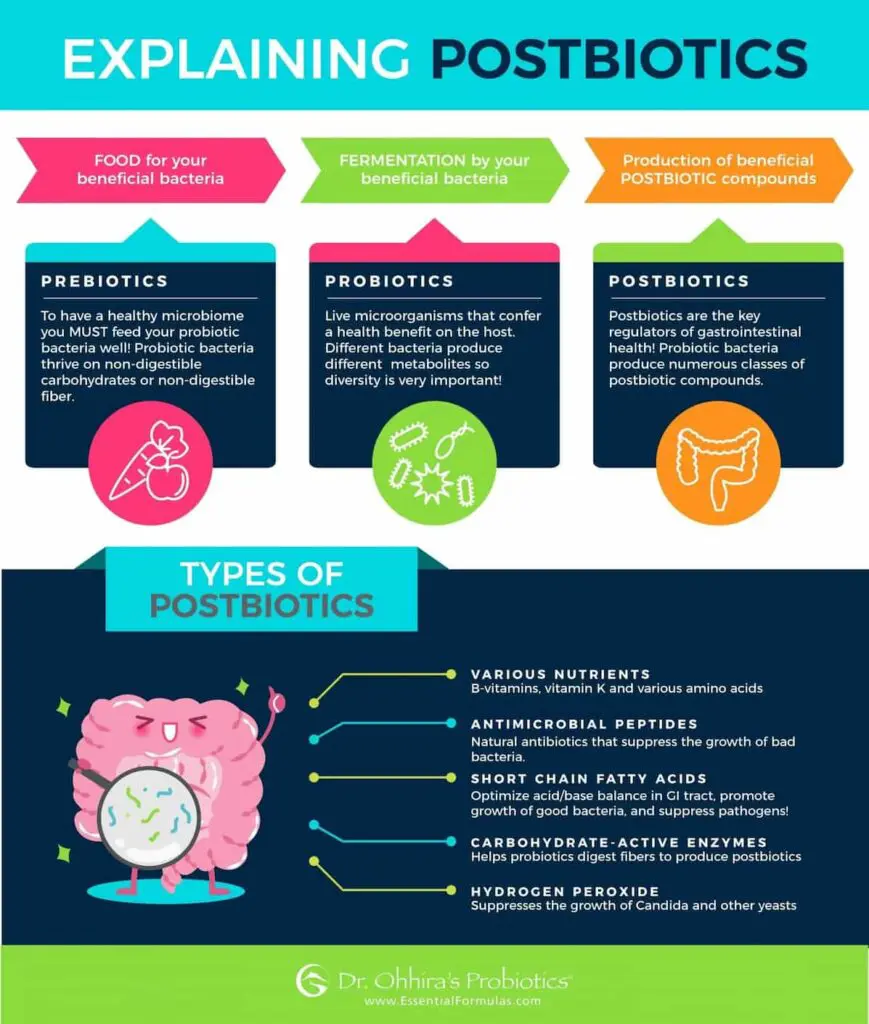
The Gut Health Trio: Prebiotics, Probiotics, and Postbiotics
These three work together to optimize your gut health:
- Probiotics: The active ingredient, live bacteria with potential health benefits.
- Prebiotics: The food for probiotics, found in fiber-rich foods like beans and oats.
- Postbiotics: The byproducts of probiotics, including vitamins, enzymes, and short-chain fatty acids.
Why are Postbiotics Important?
Postbiotics may hold the key to various health benefits:
- Improved Digestion: They might ease digestive discomfort.
- Stronger Immunity: Studies suggest they can boost your immune system.
- Balanced Inflammatory Response: They may help regulate inflammatory response.
- Enhanced Mental Wellbeing: Research indicates a potential link to improved mental health.
- Overall Health Promotion: Studies suggest they might improve sleep, reduce the effects of stress, and even influence weight management.
Boosting Your Postbiotics Naturally
The best way to get postbiotics is to support the good bacteria already in your gut:
- Eat a Fermented Food Diet: Yogurt, kimchi, kombucha, and other fermented foods are loaded with probiotics that create postbiotics.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Prebiotics in fiber-rich foods feed your gut bacteria, promoting postbiotic production.
Considerations and Next Steps
While research on postbiotics is promising, it’s still in its early stages.
If you’re interested in learning more, talk to your doctor. They can advise you on dietary changes or potential probiotic supplements to support your gut health.”
Dr. Ohhira’s Probiotics with prebiotics and postbiotics get a jump start to “Remodel Your Gut”!