Glutathione is an intriguing compound shown to do wonders for the human body. Studies have shown that increased levels of this critical nutrient could support your health and reduce the impact of certain chronic diseases.
This article aims to clarify glutathione’s benefits, risks, and side effects to help dispel the rumors and mistruths that often fly around the internet.
What Is Glutathione?
Glutathione is a naturally-occurring tripeptide made in liver cells from three amino acids: cysteine, glutamate, and glycine. It has antioxidant and cellular protective properties that are getting much attention in medical circles. Some are calling it the “master antioxidant.”
Aging and lower levels of glutathione seem to go together, and those lower levels appear to correspond with poorer health.
Top 4 Glutathione Health Benefits
Scientists have been studying glutathione over the last few years and have found multiple health benefits when its levels increase in the body. There are several ways to raise glutathione levels, which we’ll discuss later in this article.
Helps Reduce Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is a health state characterized by an overabundance of free radicals due to the body’s inability to counteract them with antioxidants. Free radicals are oxygen molecules with one or more unpaired electrons that can chemically react with DNA, proteins, or lipids to stabilize themselves, creating imbalance in the body.
Antioxidants prevent these unwanted reactions by donating a molecule to the free radicals yet staying balanced. This process neutralizes the free radicals and helps reduce oxidative stress. Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that can help improve many health conditions by reducing oxidative stress.
Supports Brain Health
The human brain consumes a great deal of oxygen, so it is highly susceptible to reactive oxygen species or free radicals. When there are sufficient levels of active antioxidants, proper brain functioning and mental acuity can be protected and enhanced. Glutathione is one of the most important antioxidants that has shown promise for brain health.
Aids Those with Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is when body cells do not respond normally to insulin. Insulin is instrumental in delivering glucose from the blood to the cells, thus reducing glucose in the blood. When this mechanism does not work correctly, it can result in metabolic syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and type 2 diabetes.
As we age, we produce less glutathione, resulting in weight management difficulties and insulin resistance. When older individuals increased cysteine and glycine consumption to increase glutathione levels, insulin resistance and fat burning improved in about two weeks.
May Benefit Athletic Performance
Exercise increases oxidative stress by increasing the amount of oxygen you consume. As discussed earlier, oxidative stress generates free radicals that damage healthy cells, produce inflammation, and make you age faster. Since glutathione is a powerful antioxidant, increasing levels in the body can lead to enhanced athletic performance, including the following:
- More energy
- Slower aging
- Reduced muscle and joint pain
- Liver and cell detoxification
- Enhanced sleep
- Decreased stress
- Improved performance and faster recovery
How to Boost Glutathione Levels
You can boost glutathione levels in several ways:
- Increase consumption of foods that stimulate glutathione production
- Take injections
- Take supplements
- Use an inhaler
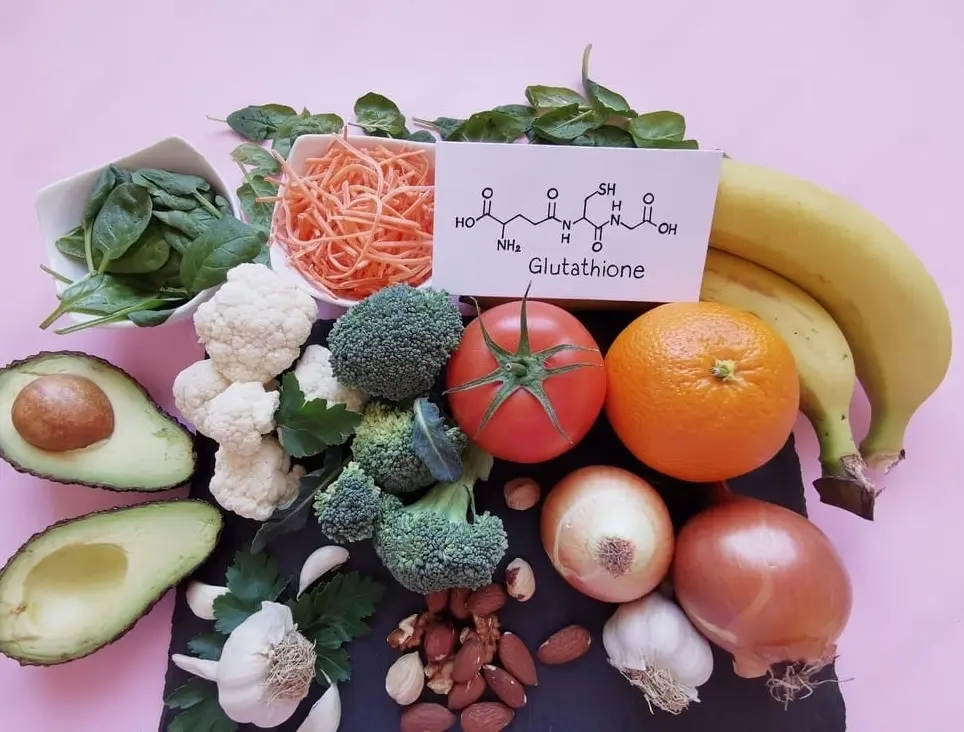
Foods That Increase Glutathione Levels
Certain foods provide the building blocks that encourage or help the body to produce more glutathione.
- Sulfur-rich foods like beef, fish, poultry, and cruciferous vegetables
- Vitamin C from citrus fruit, bell peppers, kiwis, and other fruits and vegetables
- Selenium-rich foods like Brazil nuts, organ meats, and fish
- Glutathione-rich foods such as spinach, avocadoes, asparagus, and okra
- Whey protein to increase cysteine levels
- Sufficient sleep and regular exercise
Glutathione Supplementation
You can supplement your diet with glutathione to maintain healthy cellular function, detoxify your liver, and strengthen your immune system, but know that most glutathione supplements are actually ineffective since the body will naturally break down glutathione taken orally into the three individual amino acid components during the normal digestion process. As long as the body has sufficient co-enzymes to reassemble the full glutathione molecule and isn’t under too much stress or weakened by illness or aging, some benefits can be achieved. The better options are supplements that are either liposomal forms, injections, or supplements that contain the unique probiotic strain L. fermentum ME-3, which produces glutathione directly in the intestinal tract by passing the digestive breakdown in the stomach. Do your research and make sure the source is reliable and reputable.
What Causes Glutathione Deficiency?
Several conditions and habits can contribute to glutathione deficiency. Here is a small selection:
- Aging
- Environmental pollution
- Smoking
- Viruses
- Overexercising
- Gene mutations
- Poor diet
- UV exposure
- Chemicals and solvents
Risks and Potential Side Effects
As with any supplement or medicine, glutathione has associated risks and side effects. We’ve listed a few below. See your doctor if you take glutathione supplements and experience these symptoms.
- Lower zinc levels
- People with asthma may experience attacks if using an inhaler
- Allergic reaction
- Dizziness or passing out
- Pale skin
- Abnormal heartbeat
Support Healthy Liver Function
Every cell in the body uses glutathione, and it is essential for liver function. Essential Formulas’ Reg’Activ line of products provides the L. fermentum ME-3 probiotic strain plus some condition-specific nutritional elements that support general health (Essential ME-3), liver health (Liver & Detox), immune support (Immune & Vitality) and cardiovascular support (Cardio-Wellness). You can order Reg’Activ products online.